The budget at-completion calculator is a powerful tool for project managers to estimate the total cost of completing a project.
It takes into account the actual costs incurred so far and forecasts the remaining expenses based on various factors.
The budget at completion (BAC) is calculated by adding the actual costs (AC) to the estimated costs to complete the remaining work (ETC). This formula, BAC = AC + ETC, provides project managers with a clear picture of the project’s financial health.

In this article, we’ll explore the importance of the budget at completion calculator, how to calculate it, interpret the results, and integrate it into your project management processes.
We’ll also cover best practices, case studies, and examples to help you master this essential tool.
What is the Budget at Completion Calculator?
The BAC calculator is a powerful tool that helps project managers estimate the total cost required to complete a project.
It takes into account the actual expenses incurred so far and forecasts the remaining costs based on various factors. In other words, it’s like having a crystal ball that lets you peek into the future and plan accordingly.
Why is the BAC Calculator Important?
Have you ever found yourself in a situation where a project’s budget spiraled out of control, leaving you scrambling to find additional funds or, worse, facing the dreaded prospect of cancellation?
The BAC calculator is designed to prevent such nightmares. By providing an accurate estimate of the total costs, it allows you to:
- Monitor spending: Keep a close eye on your spending so far and how much more you’ll need to allocate.
- Identify potential issues: Spot potential budget overruns early on, giving you the opportunity to make adjustments or seek additional funding.
- Enhance decision-making: Armed with accurate cost projections, you can make informed decisions about resource allocation, scope changes, or even project feasibility.
In essence, the BAC calculator empowers you to take control of your project’s financial health, ensuring that you stay on track and deliver within the allocated budget.
Calculating the Budget at Completion
Now, let’s explore how the BAC calculator works. Imagine it as a simple yet powerful formula that considers various factors to give you an accurate estimate of the total costs.
Budget at Completion Formula
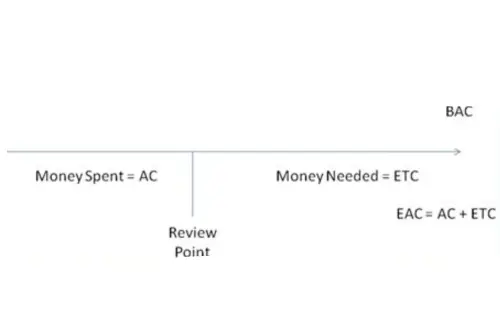
The BAC formula is as follows:
BAC = AC + ETC
Where:
- BAC (Budget at Completion) is the total estimated cost to complete the project.
- AC (Actual Cost) is the cost incurred so far on the project.
- ETC (Estimate to Complete) is the estimated cost required to finish the remaining work.
Seems straightforward, right? But don’t be fooled by its simplicity. The real challenge lies in accurately estimating the ETC, which requires careful analysis of various factors, such as:
- Remaining scope of work
- Resource availability and costs
- Historical data from similar projects
- Risk factors and contingencies
Interpreting the Results
Once you’ve plugged in the numbers, the BAC calculator will provide you with a final figure – the estimated total cost to complete your project. But what do you do with this information? Here’s how you can interpret the results:
- If the BAC is lower than the original budget, Congratulations! You’re on track to complete the project under budget. This could be an opportunity to reallocate funds or even finish ahead of schedule.
- If the BAC is higher than the original budget, Brace yourself, as this could indicate potential cost overruns. It’s time to investigate the root causes and explore options such as scope adjustments, resource optimization, or seeking additional funding.
- If the BAC matches the original budget, You’re right on target! Keep up the good work, and maintain close monitoring to ensure you stay within budget.
Budget at Completion Example
Let’s illustrate this with a practical example. Imagine you’re managing a software development project with an initial budget of $500,000.
So far, you’ve incurred $250,000 in actual costs. Your team has estimated that completing the remaining work will cost an additional $275,000.
Using the BAC formula:
BAC = AC + ETCBAC = $250,000 + $275,000BAC = $525,000
In this case, the BAC of $525,000 is higher than the original budget of $500,000, indicating a potential cost overrun of $25,000.
This information would prompt you to investigate the reasons behind the increased costs and take appropriate actions, such as negotiating with vendors, optimizing resource allocation, or seeking additional funding from stakeholders.
Integrating BAC into Project Management
The BAC calculator is not a standalone tool; it’s most effective when integrated into your overall project management strategy. Here’s how you can seamlessly incorporate it into your processes:
- Budget planning: During the initial project planning phase, use historical data and expert estimates to create a realistic budget baseline. This will serve as the foundation for your BAC calculations.
- Cost tracking: Implement robust cost tracking mechanisms to capture actual costs as they are incurred accurately. This data will feed into the AC component of the BAC formula.
- Regular updates: Periodically update your BAC calculations, taking into account any changes in scope, resource availability, or other factors that may impact the ETC.
- Reporting and communication: Share the BAC results with stakeholders, highlighting any potential issues or opportunities. This transparent communication will foster trust and collaboration.
By integrating the BAC calculator into your project management processes, you’ll gain a holistic view of your project’s financial health. This will enable proactive decision-making and increase the chances of successful project delivery.
Best Practices for Using the BAC Calculator
To maximize the effectiveness of the BAC calculator, consider adopting the following best practices:
- Accurate data: The quality of your BAC calculations depends on the accuracy of the input data. Ensure that your cost-tracking and estimation processes are robust and reliable.
- Collaboration: Involve key stakeholders, such as subject matter experts and team members, in the estimation process. Their insights and experience can improve the accuracy of your ETC calculations.
- Contingency planning: Account for potential risks and uncertainties by including contingency reserves in your BAC calculations. This will help you better prepare for unexpected events.
- Regular reviews: Continuously monitor and review your BAC calculations, adjusting them as necessary based on project progress and changes in scope or assumptions.
- Automation: Consider using project management software or specialized tools that can automate the BAC calculation process, reducing the risk of manual errors and saving time.
By following these best practices, you’ll enhance the reliability and effectiveness of your BAC calculations, ultimately increasing your chances of delivering projects on time and within budget.
Case Studies and Examples
To fully appreciate the power of the BAC calculator, let’s explore some real-world case studies and examples:
Example 1: Construction Project
A construction company was tasked with building a new office complex with an initial budget of $10 million.
By regularly calculating and monitoring the BAC, the project manager identified potential cost overruns early on due to unforeseen site conditions and material price increases.
Armed with this information, the company was able to negotiate with suppliers, optimize resource allocation, and secure additional funding from the client, ultimately completing the project within the revised budget.
Example 2: IT Infrastructure Upgrade
An IT company embarked on a significant infrastructure upgrade project with a budget of $2 million. By incorporating the BAC calculator into their project management processes, the team quickly identified that the initial budget was too optimistic.
They proactively communicated this to stakeholders and worked collaboratively to adjust the scope and timeline, ensuring a successful project delivery within the revised budget constraints.
Example 3: Marketing Campaign
A marketing agency was tasked with executing a multi-channel campaign for a client with a budget of $500,000.
By regularly calculating the BAC, the project manager noticed that the actual costs for certain activities, such as influencer marketing and video production, were higher than initially estimated.
This early warning allowed the agency to reprioritize tasks and reallocate resources, ensuring they delivered a successful campaign within the client’s budget.
These examples illustrate the versatility and effectiveness of the BAC calculator across various industries and project types.
By incorporating it into your project management practices, you’ll be better equipped to navigate financial challenges, manage stakeholder expectations, and ultimately increase your chances of project success.
Conclusion
The Budget at Completion calculator is a powerful tool that should be in every project manager’s arsenal.
Providing accurate cost projections and enabling proactive decision-making can help you confidently navigate the financial complexities of project management.
Remember, the key to unlocking the BAC calculator’s full potential lies in accurate data, collaboration, contingency planning, regular reviews, and, where possible, automation.
By embracing these best practices, you’ll be well on your way to mastering the art of budget management and delivering projects that not only meet stakeholder expectations but also stay within the allocated financial resources.
So, why wait? Embrace the BAC calculator today and take your project management skills to new heights.
With this trusty tool by your side, you’ll be able to confidently steer your projects through any financial challenges that may arise, ensuring successful outcomes time and time again.
[su_button Id= download url=”https://selffinance.info/whats-your-budget/” target=”blank” size=”10″]CLICK HERE[/su_button]
How do you calculate the total budget at completion?
The total budget at completion (BAC) is calculated by adding the actual costs incurred so far (AC) to the estimated costs required to complete the remaining work (ETC). The formula is:
BAC = AC + ETC
How do you calculate cost at completion?
The cost at completion is the same as the budget at completion (BAC). It refers to the total estimated cost required to complete the project, including both the actual costs incurred so far and the estimated costs to finish the remaining work.
What is the budgeted cost at completion?
The budgeted cost at completion, also known as the budget at completion (BAC), is the total approved budget for the project. It represents the maximum authorized funds allocated to complete the project.
What is the EAC formula?
The EAC (Estimate at Completion) formula is used to calculate the expected total cost of the project based on the actual performance to date. The formula is:
EAC = AC + (BAC – EV) / (EV / AC)
Where:
AC = Actual Cost
BAC = Budget at Completion
EV = Earned Value
The EAC provides an updated estimate of the total project cost, taking into account any deviations from the initial budget.






1 thought on “The Ultimate Guide to the budget at completion calculator”